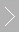
In-situ Electrochemical Mass Spectrometer (Electrocatalysis DEMS)
QAS 100 Plus

QAS 100
Differential Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry (DEMS) is an in-situ electrochemical method that provides qualitative and quantitative information about the interface by detecting volatile products. It has become an indispensable tool in studying the mechanisms of electrochemical reactions. The DEMS system combines an electrochemical reaction setup with a mass spectrometer. Volatile products generated during the electrochemical reaction pass through a hydrophobic and gas-permeable membrane interface and enter the vacuum system of the mass spectrometer. The current of different mass-to-charge ratio ions is then recorded over time.
Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) is a commonly used electrochemical technique in the study of electrochemical reaction mechanisms. Rich electrochemical information can be obtained from the CV curves. As a result, CV is frequently used in DEMS research. During electrochemical research using DEMS, the mass spectrometer detects the ion current signals of the volatile products generated during the CV scanning process over time. By transforming these signals from the time axis to the potential axis, the Mass Spectrometric Cyclic Voltammogram (MSCV) is obtained, providing more comprehensive and in-depth information for the study of electrocatalytic reaction mechanisms.
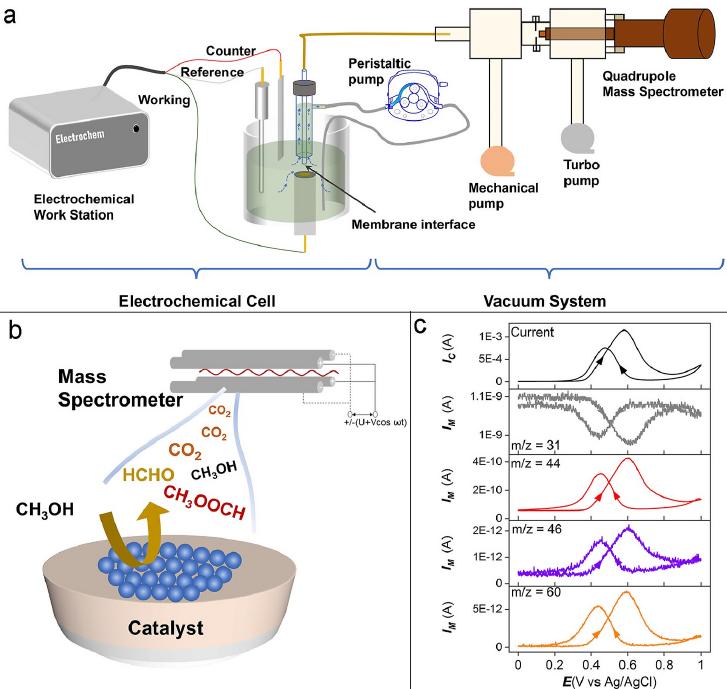
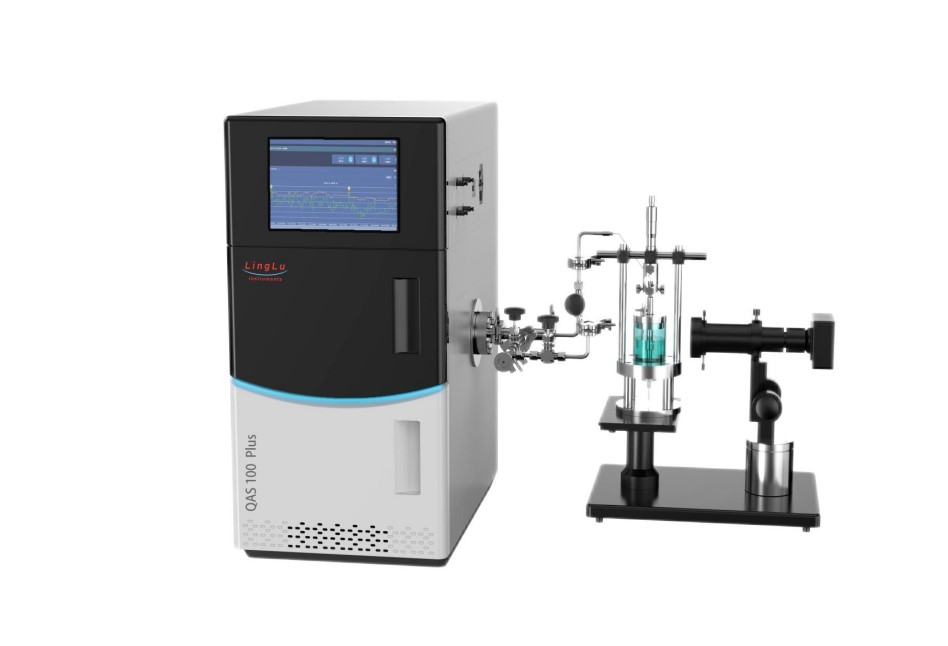
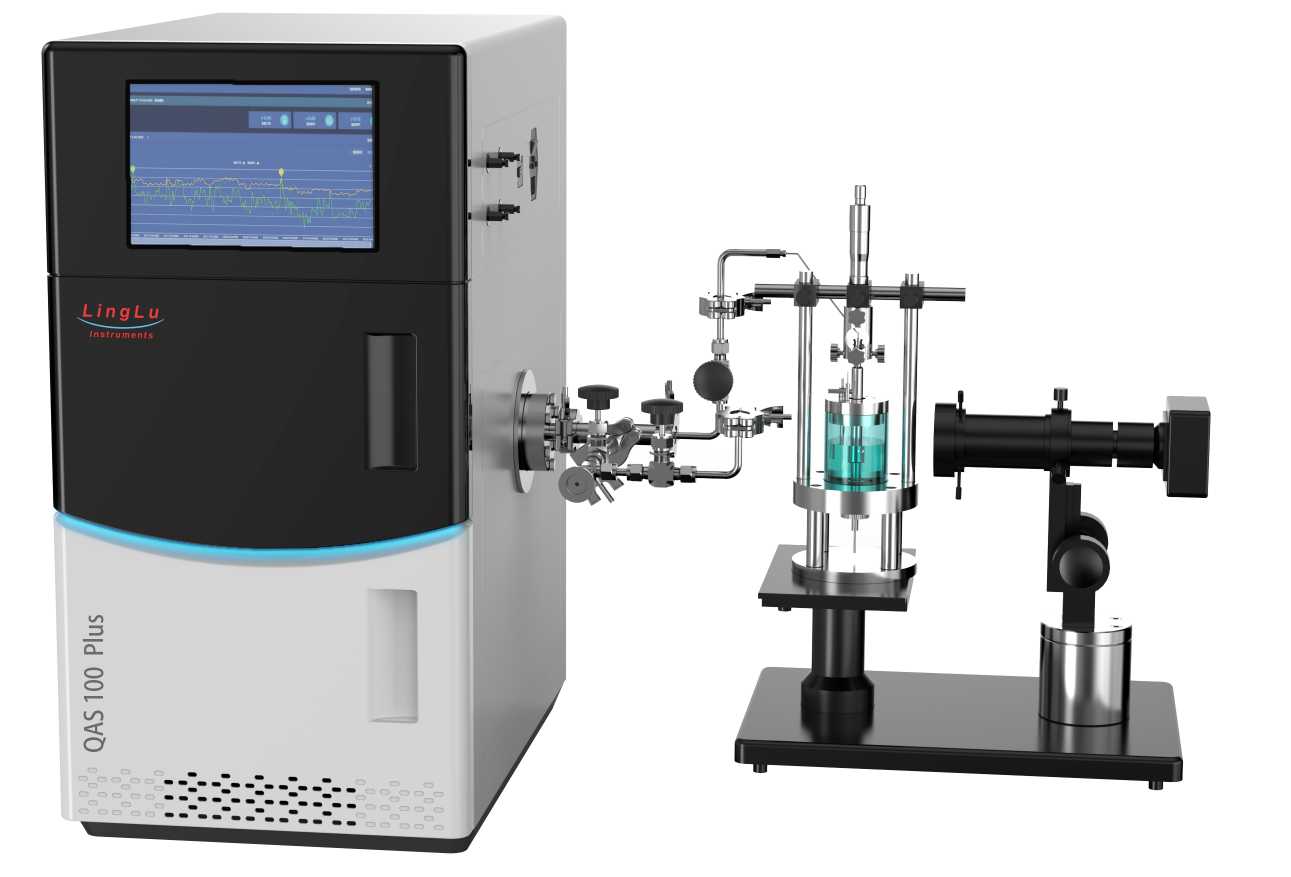
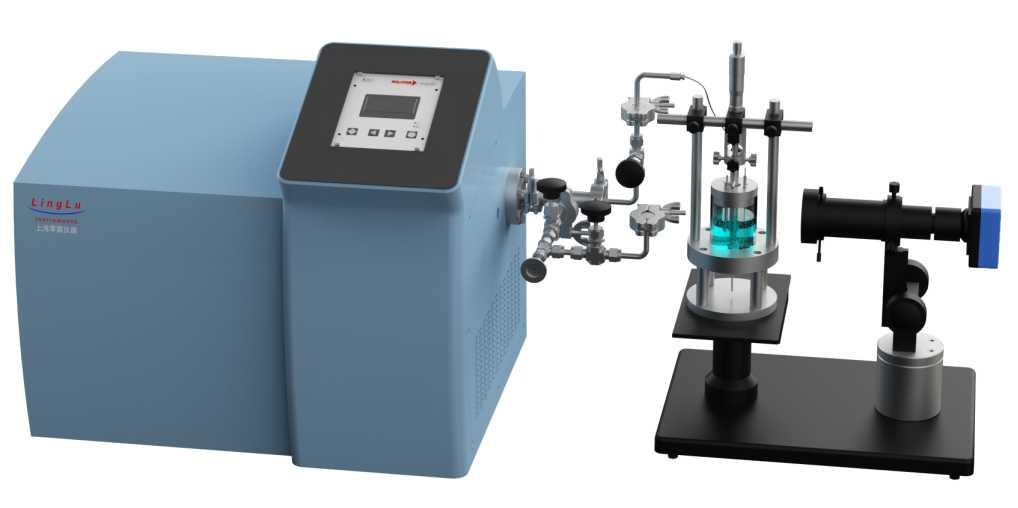
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of the Probe-based In-situ Differential Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry (DEMS) System.
Structure Composition: The system consists of a Mass Spectrometry Sampling Probe and a glass electrochemical cell.
Working Principle: The Mass Spectrometry Sampling Probe is positioned facing the working electrode in the glass electrochemical cell. The products generated on the working electrode are transferred through the probe's end filter membrane and detected by the mass spectrometer. A video microscope is used to precisely adjust the distance between the sampling probe and the working electrode.
Main Features:
1. Suitable for both flowing and static systems.
2. High collection efficiency and sensitivity.
3. Particularly suitable for single crystal electrodes.
4. Capable of multi-coupling with surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy.
Specific Applications Include:
1. Instantaneous detection of gas-phase products (CO, CH4, C2H4, CH3OH, etc.) in CO2 electrocatalytic reduction and relative Faradaic efficiency determination.
2. In-situ detection of intermediate or final products (NO, N2O, NH2OH, NH3, N2, etc.) in nitrate electrocatalytic reduction.
3. Confirmation of OER (Oxygen Evolution Reaction) mechanisms with isotopic labeling of 18O in water electrolysis, LOM (Light Oxygen Molecule) or AEM (Anionic Exchange Membrane) reactions.
4. Instantaneous detection and current efficiency calculation of intermediate or final products (HCHO, HCOOH, CO, etc.) in methanol electrooxidation reactions.
5. Mechanistic analysis of hydrogen evolution reactions (HER) with hydrogen isotope labeling.
6. Evaluation of carbon materials' stability under high potential (CO and CO2 detection).
7. Other applications include photocatalysis, photoelectrocatalysis, oxygen reduction, hydroxide generation, chlorine evolution, organic electrosynthesis, and more.
Application Case:
1. Nitrate anion electrochemical reduction intermediate detection.
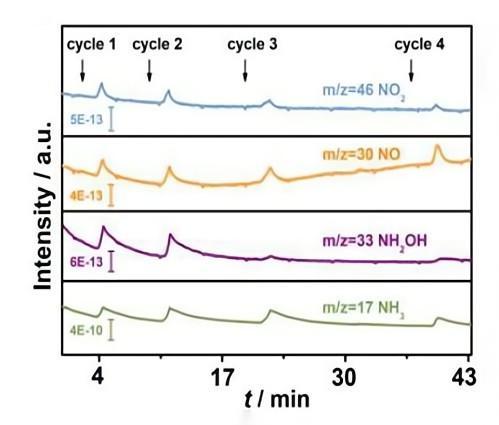
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10.1002/anie.201915992
2. Electrolysis of water for OER isotope labeling with 18O, and confirmation of LOM or AEM reaction mechanism.
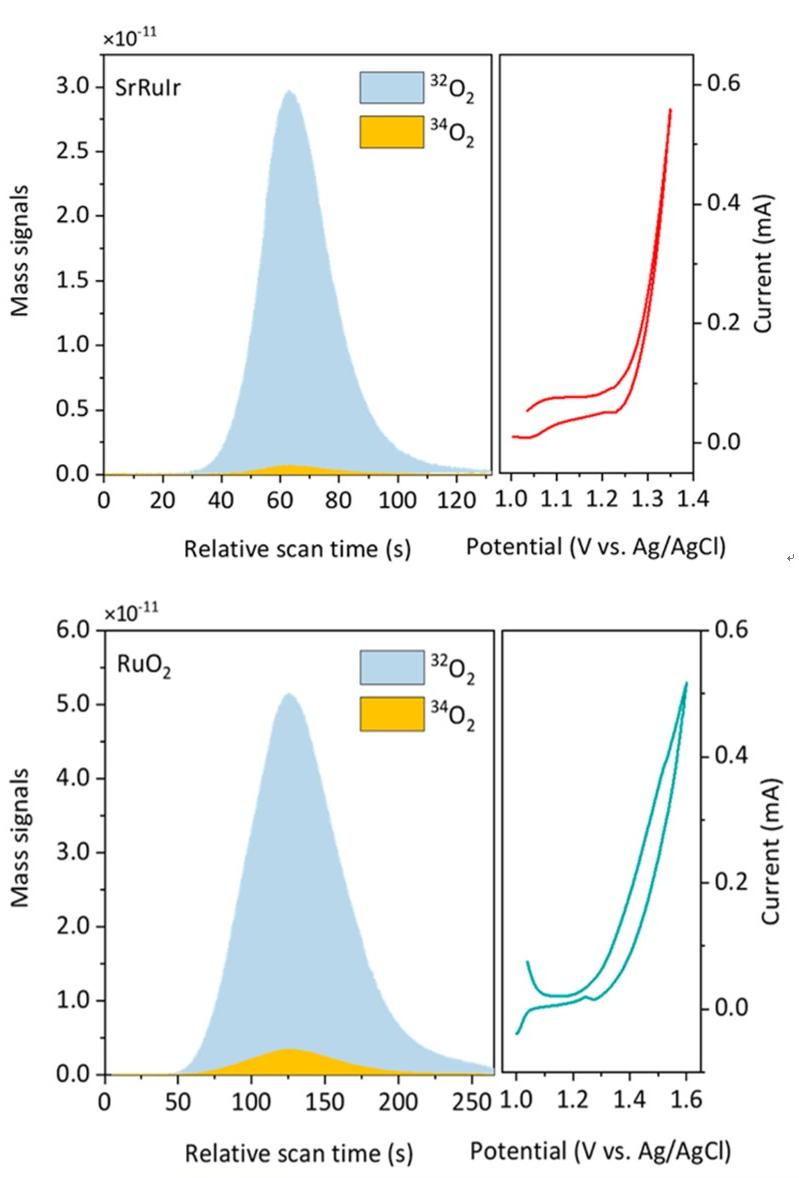
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17, 6482-6490
3. Methanol electrocatalytic oxidation reaction.
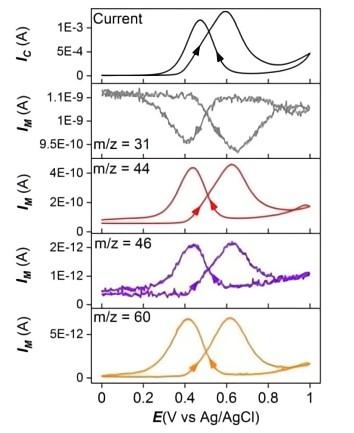
Journal of Power Sources 509 (2021) 230397
4. Hydrogen isotope labeling and mechanistic analysis of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) with hydrogen gas evolution.
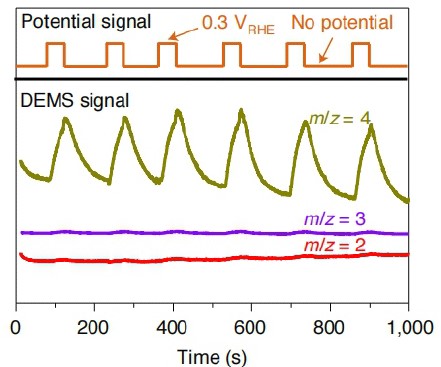
Nature catalysis, 2022,5,66-73
5. Electrochemical reduction of CO2.
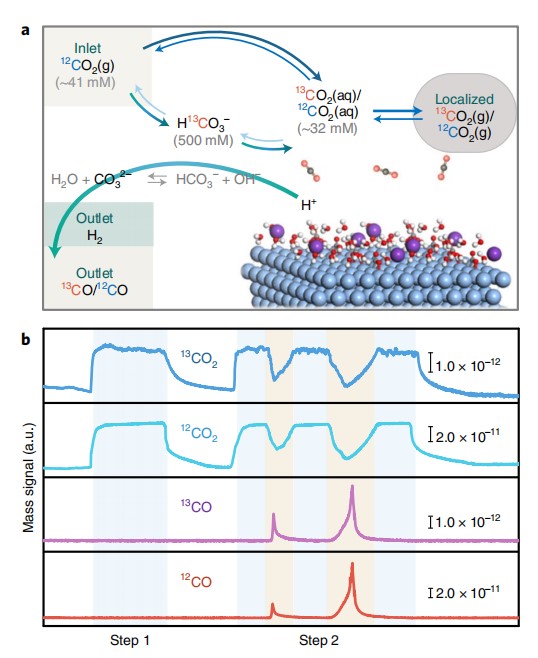
ACS catal. 2019,9,1383-1388
Partial Customer Paper List:
Nature Catalysis. 2022, 5, 66-73
Nature Catalysis. 2021, 4, 1012-1023
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6482-6490
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9444-9447
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5350-5354
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 4670-4674
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7297-7307
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22933-22939
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26177-26183
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, e202204541
Joule. 2021, 5, 2164-2176
Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2191
Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2164
Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002297
Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001289
Appl. Catal. B. 2021, 280, 119393
ACS Energy Letters. 2022, 7, 1187-1194
ACS Energy Letters. 2022, 7, 284-291
Chem. Eng.J. 2022, 435, 134969
Chem. Eng.J. 2022, 433, 133495
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 614-623
ACS Catal. 2021,11, 840-848
ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4699-4705
Nano Energy. 2021, 86, 106088
NanoEnergy. 2019, 60, 43-51
ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14032-14037
ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 3533-3540
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022, 14, 12257-12263
J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 239-243
Cell Reports Physical Science. 2021, 2, 100378
J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 9010-9017
Journal of Catalysis. 2021, 397, 128-136
Journal of Power Sources. 2021, 509, 230397
Science China Chemistry. 2020, 63, 1469-1476
Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2020, 4, 2000227
Science China Chemistry.2021, 64, 1493-1497
J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 614, 405-414
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e20211563
Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2577
J. Mater. Chem. A. 2022, 10, 6448–6453
J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 14741–14751
ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 5958–5965
J. Mater. Chem. A. 2022, 10, 5430-5441
Appl. Catal. B. 2022, 301, 120829
Adv. Mater. 2020, 2202523
Adv. Mater. 2020, 2202874
ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 14, 8658–8666
Energy Environ. Sci. 2022,15, 3912-3922
Adv. Mater. 2022, 2209307
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202217071
ACS Nano. 2022, 16, 6, 9095–9104
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212341
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 35, 16006–16011
Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103960
Nature Energy. 7, 978–988 (2022)
Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 4175
Nat. Commun. (2022) 13:7958